Sensors Used in Agricultural Machinery and Their Advantages
Introduction
In the realm of modern agriculture, sensors have become indispensable tools, revolutionizing farming practices and enhancing productivity. These devices play a crucial role in monitoring various environmental and operational parameters, enabling farmers to make informed decisions and optimize resource use. This article explores the different types of sensors employed in agricultural machinery and their significant advantages.
Types of Sensors and Their Applications
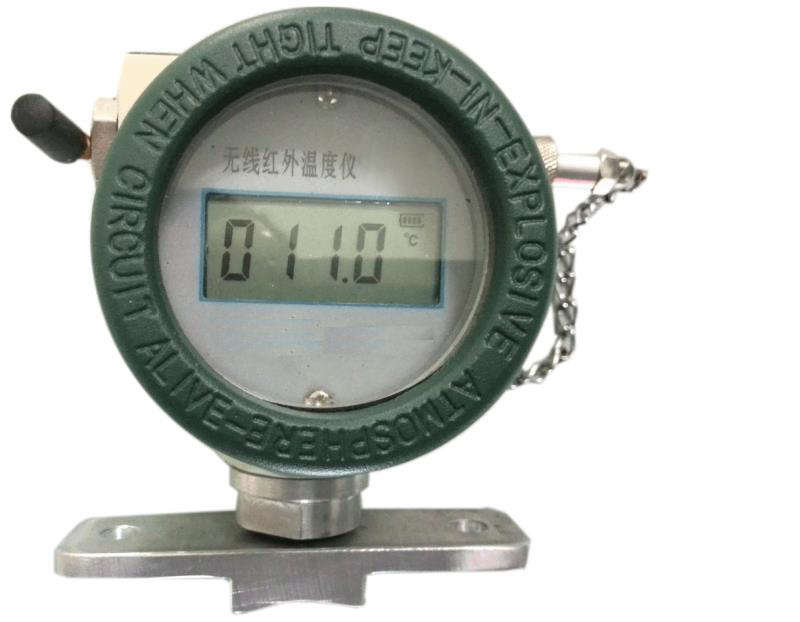
Temperature Sensors
Application: Temperature sensors are integral to monitoring environmental conditions, such as air and soil temperature, which directly influence crop growth and livestock health.
Advantages: They ensure optimal growing conditions, prevent frost damage, and help maintain comfortable temperatures for animals, thereby improving productivity.

2.Humidity Sensors
Application: These sensors measure moisture levels in the air and soil, crucial for irrigation management.
Advantages: They prevent over-irrigation, conserve water, and protect crops from moisture-related stress, reducing waste and enhancing yield.
3.Pressure Sensors
Application: Used to monitor pressure within machinery, such as in pneumatic systems or liquid delivery.
Advantages: They ensure efficient operation of machinery, prevent equipment failure, and optimize performance.

4.Light Sensors
Application: These sensors detect lensors detect light intensity, aiding in the automation of lighting systems for greenhouses or vertical farming.
Advantages: They provide consistent light levels, optimize photosynthesis, and reduce energy consumption by activating lights only when needed.

5.Soil Sensors
pH Sensors: Measure soil acidity, helping farmers adjust pH levels for optimal nutrient absorption.
EC (Electrical Conductivity) Sensors: Monitor soil fertility and salinity, guiding precise fertilizer application.
Moisture Sensors: Track soil moisture content to prevent under or over-irrigation.
Advantages: Together, these sensors enable precision agriculture, reduce resource waste, and improve crop health.
6.Speed and Position Sensors
Application: These sensors monitor the speed and position of machinery, essential for accurate planting and spraying.
Advantages: They enhance operational efficiency, reduce overlap, and ensure even distribution of seeds and chemicals.

7.Gas Sensors
Application: Detect gases like methane or carbon dioxide in greenhouses, crucial for maintaining optimal growing conditions.
Advantages: They prevent harmful gas buildup, improve air quality, and support healthier plant growth.
8.Weight Sensors
Application: Used in machinery for weighing materials like seeds or fertilizers.

Advantages: They ensure accurate measurements, prevent waste, and support precise application of inputs.
Conclusion
The integration of sensors into agricultural machinery has ushered in a new era of precision and efficiency in farming. By providing real-time data and insights, these sensors empower farmers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and enhance productivity. As technology continues to advance, the role of sensors in agriculture will expand, driving sustainable practices and contributing to global food security. Embracing these technologies is not just a step forward; it's a necessity for modern, efficient farming.
Recently Posted
-
Why Elevator Weight Measurement Equipment Is Essential for Modern Buildings
October 17, 2025Elevators are an essential part of modern buildings, providing efficient vertical transportation in residential, commercial, and i Read More
Read More -
Elevator Load Sensors: Choosing the Perfect Fit for Your System
October 15, 2025How to Choose the Right Load Sensors for Elevators: A Comprehensive GuideElevator load sensors are critical components that ensure Read More
Read More -
Top Tips for Finding the Most Cost-Effective Elevator Weight Measurement Systems
October 11, 2025How to Find the Most Cost-Effective Elevator Weight Measurement SystemsWhen it comes to selecting elevator weight measurement syst Read More
Read More -
Enhance Elevator Safety: A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing Weight Measurement Equipment
October 10, 2025How to Choose the Right Elevator Weight Measurement EquipmentElevators are essential components of modern buildings, and ensuring Read More
Read More





















